Learn about the electrification of heat and all you need to know.
The use of cleaner, renewable power to heat homes is referred to as electrified heating. Because the energy system is quickly decarbonizing, emissions from electric heating are reducing and will continue to reduce.
Some contend, however, that because electricity costs are now higher than gas, electrification for heating could result in increased home energy bills. Power rates are frequently higher than gas bills due to additional taxes and levies imposed on electricity as opposed to gas.
This includes support for measures that encourage the use of renewable energy and reduce energy waste, as well as carbon levies that are not imposed on domestic gas. Because of this, it is essential to look out for other technologies, to calm the situation. Learn about electrolyzer and all you need to know.
Meaning of Electrification
Electrification is defined as the process of replacing fossil-fuel-based technologies (such as coal, oil, and natural gas) with electricity-based technology.
Another approach to thinking about electrification is as a strategy to reduce carbon emissions from ultimate energy usage in transportation, buildings, and industries. To reach carbon neutrality by 2050, all of these sectors must be electrified.
GHG emissions are reduced, an affordable and secure energy supply is ensured, energy efficiency is increased, urban air quality is enhanced, and new, high-quality jobs are created as a result of a well-planned and equitable transition. Last but not least, electrification can aid in the fight against global warming. Explore the long duration of energy storage in Nigeria.

Electrification of Heat Sources/Technologies
There are various sources/technologies that can electrify heating, some more proven than others. The Electrification of Heat Demonstration Project is underway, with the goal of determining the hurdles to home adoption of certain electric heating technology.
The widespread electrification of heat outside the home will necessitate a lot of infrastructure changes. To make the system smarter and more efficient, reinforced power grids, new generating technology, and digital infrastructure will be required. This is similar to the challenges that have arisen as a result of the electrification of transportation.
Read- Battery recycling and all you need to know.
3 Electric Heating Technologies
The following are Electric Heating Technologies:
- Electric (resistance) Heaters
An electrical resistor converts an electric current into heat, which is how resistance heating works. Electric radiators are already used in some new homes. And many more use portable heaters to supplement heat during exceptionally cold weather.
Resistance heaters are approximately 100% efficient and may be turned on and off as needed, just like a gas boiler. While this familiarity might be beneficial to customers, it can also lead to demand spikes. And, given current electricity prices, this form of electric heating can be costly.
- Electric Storage Heaters
Storage heaters use resistance to generate heat, which is then stored in ceramic blocks and released when needed. Storage heaters account for roughly two-thirds of the current electric heating stock in some countries.
Because they can store heat, they can run when electricity is cheapest and cleanest, which is usually overnight, while still providing heat when needed. This storage capability might potentially be used to help balance the electrical grid, generate cash or lower rates. Learn about electric equipment and how to maintain it.
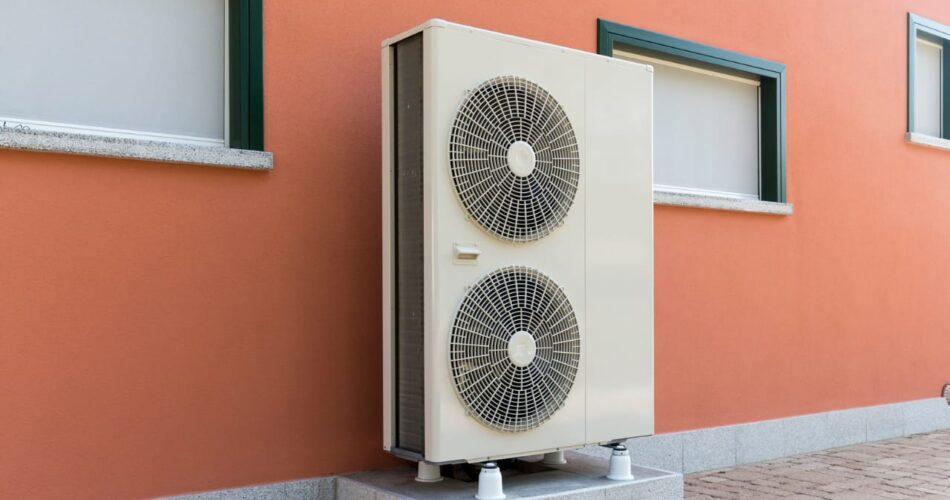
- Heat Pumps
Heat pumps use a compressor and a condenser to take ambient heat from the earth, air, or water and increase it to a much higher temperature.
They are highly efficient because of this concentration of heat, producing three units of heat for every unit of energy consumed. Heat pumps are much more cost effective, and less carbon intensive than resistance heaters. They do, however, perform best in very well insulated homes.
Besides that, they are typically designed to run at lower temperatures but continuously, offering a different customer experience than gas boilers.
Experts agree that the use of heat pumps will undoubtedly increase, with some predicting that 1 million will be required yearly by the mid-2030s.
Heat pumps are currently available for purchase, resulting in immediate reductions in emissions. On the other hand, low-carbon gases are still being produced.
What Do Uses of Electrification Mean?
Using electricity to supply services that were previously provided by other energy sources, such as fossil fuels, is referred to as electrification of uses. Electrification of usage is exemplified by electric cars and buses.
Another example is the electrification of building energy use. By deploying heat pumps and other interventions, the share of electricity in final energy demand in this sector will rise from 42% in 2030 to 72 percent by 2050. By promoting easy electrification in buildings, fossil fuels for heating will progressively be phased out.
Read- Geothermal Heating- How it works and How long it lasts.
Conclusion
With today’s extremely efficient heat pump technology, heating electrification helps to convert “free” energy into useful heat for building with only a little power input. Electrification Heat sources solve the problem of high electricity costs, which are now higher than gas.
Therefore, it is essential to implement the electrification heat sources/technologies discussed in this article to calm the situation.
Related Post:
Plastic recycling and everything you need to know.